About Coin Collecting
Order & Shipping
Services
How To Select Magnifiers
Precision work routinely requires magnification to increase the visual size of objects. As the eye comes closer to an object, the apparent size and detail is increased. However, the ability of the eye to focus correctly diminishes at distances closer than 10" (254 mm). Use of a magnifier provides increased focusing power, resulting in the visual effect of a clearer, larger image of the object.
Four Characteristics Of Magnifiers
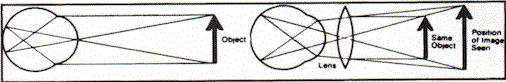
1) Power of Magnification - The ability of the lens to increase the visual size of an object. The symbol X (times) is used to identify this factor. For example, a 3X magnifier triples the size of an image.
- Light rays are bent by the curved lens surface resulting in an image that looks larger than the actual object.
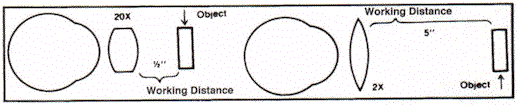
2) Working Distance (Focal Length) - In addition to power, a magnifier will also be classified for working distance. For example, 2X at a working distance of 5" (127 mm), means that the magnifier will provide double magnification and be in clear focus when held at a distance of 5" (127 mm) from the object.
- The amount of space between the object and the magnifier; the shorter the working distance, the higher the power.
3) Field of View - The size of the area that is seen through the magnifier; the field of view decreases as the power increases.
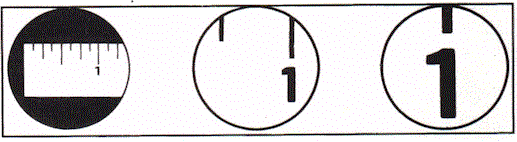
4) Depth of Field - The distance that a magnifier can be moved form an object and still have the object in focus; the higher the power, the shorter the depth of field.
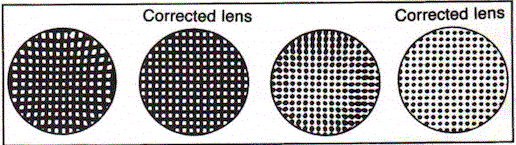
Corrective Magnifiers - Certain magnifiers have lens systems which correct optical distortion of aberration that might otherwise be present as follows:
- Distortion - Uncorrected lens - "straight lines" curve toward center.
- Chromatic and Spherical Aberration - Uncorrected lens-size and shape differences occur in a pattern consisting of on size dot.
Common Terms
Achromatic - Lens that eliminates chromatic aberration.
Aplanatic - Lens that corrects for spherical aberration and coma.
Chromatic Aberration - Inability of a lens to focus light of different colors at a point.
Coma - Blurry appearance around an object viewed through uncorrected lens.
Corrected - Lens system that corrects for distortions and aberrations to produce a sharp image.
Spherical Aberration - Lens defect that produces an image that lacks contrast.
